Image Compression: What is and How to Use It
These days, digital images are the most expressive form of online content. In actuality, they flood every individual’s devices and online spaces. However, using images with large file sizes can make the devices and platforms hard to load. Fortunately, you can overcome this struggle by using compression methods. This technique enables efficient storage and transmission of images without excessively affecting the quality. In this blogpost, we will cover the principles and applications of image compression. This way, you will gain knowledge on what compression you should use on your image file. Continue to the following section below for more details!

Contents:
Part 1. What is Image Compression?
Before we explore further, let us first broaden our understanding of image compression. Basically, it is the process of minimizing digital image file size without excessive loss of quality. This can be accomplished by utilizing algorithms to remove unnecessary and redundant data. Its goal is to save storage space and reduce the loading times required to transmit images over networks. Efficient file compression can improve a platform’s performance that relies on image data. This includes multimedia systems, mobile applications, and websites. Not to mention, compression depends on the type of image file you are using. Basically, there are two types based on which image files are categorized. These are lossless and lossy compression.
Lossless Compression
Lossless image compression technique reduces image file size without losing its original quality. This means when an image is decompressed, there is no loss of data during the process. The image will remain exactly the same as the original in terms of data and quality. This technique is vital in platforms where every single piece of data is important. One of its primary advantages is that it maintains the quality of the original image file. But here’s the thing. Lossless compression has lower compression ratios, which make image bigger in quality and size.
Lossy Compression
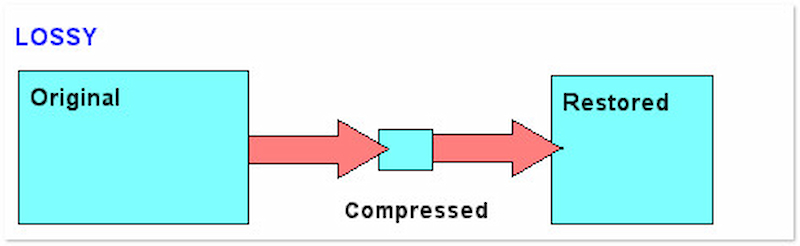
On the other hand, lossy compression uses a different technique to reduce image file size. Lossy image compression optimizes image file size by permanently discarding some of its data. It identifies and removes less important information that is less noticeable to the human eye, resulting in a loss of quality. Despite that, it can still achieve a much higher compression ratio compared to a lossless technique. Now, a small heads-up: Excessive compression using this technique can lead to a perceptible degradation in image quality.
Lossy Vs. Lossless Comparison

Both lossy and lossless compression share the characteristic of decreasing the digital image file size. Still, there is a difference between lossy vs. lossless compression techniques, particularly in handling data. The lossless compression method ensures that the original file is perfectly reconstructed from the optimized file. However, keep in mind that this technique results in larger file sizes. Meanwhile, lossy compression achieves greater file size reduction but with minimal quality loss. This technique is acceptable for web images and platforms that prioritize smaller file sizes than quality. Remember, consider your specific needs for quality, size, and storage capacity when choosing between these two compression techniques.
Common Image Compression Technique
Image compression algorithms are important for condensing digital image file sizes. These algorithms work by discarding redundancies and irrelevant data, allowing images to maintain quality while the file size is reduced. In this section, we will explore these common algorithms that can be used in various use cases.
Transform Coding
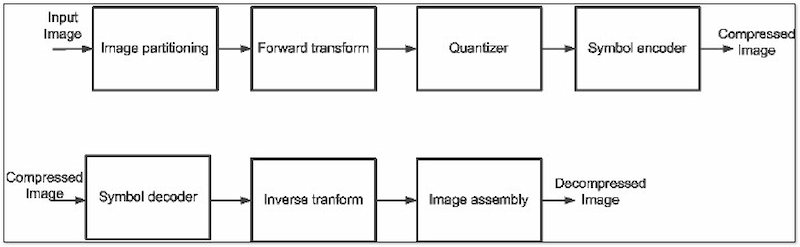
First, let’s have the commonly used compression technique, Transform coding. It works by converting an image from the spatial domain into the frequency domain. Transform coding algorithms like Discrete Cosine Transform analyze the image in the frequency domain. They can then discard less important high-frequency details that might not be readily noticeable.
LZW (Lempel-Ziv-Welch)
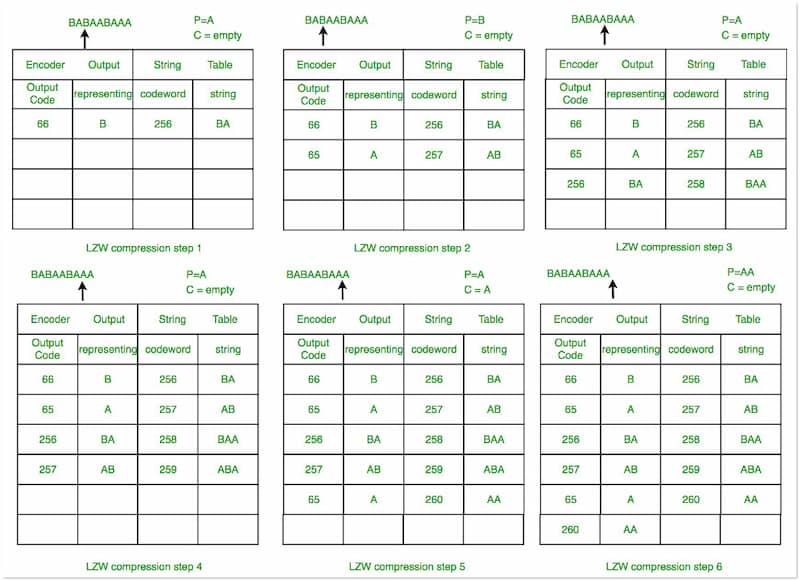
As we continue, let’s proceed to Lempel-Ziv-Welch or LZW. It identifies and replaces recurring patterns with shorter codes. It works by creating a dictionary on-the-fly as it compresses the data. When a recurring pattern is encountered, it’s replaced with a reference to its corresponding code in the dictionary, effectively reducing redundancy.
Run-length Encoding (RLE)

Next, let’s look at Run-Length Encoding. This photo compression technique identifies and encodes sequences of repeating data within an image. For example, a sequence of 20 white pixels followed by 15 black pixels would be encoded as (20W, 15B). RLE is particularly effective for images with flat areas of uniform color or simple patterns.
Huffman Coding
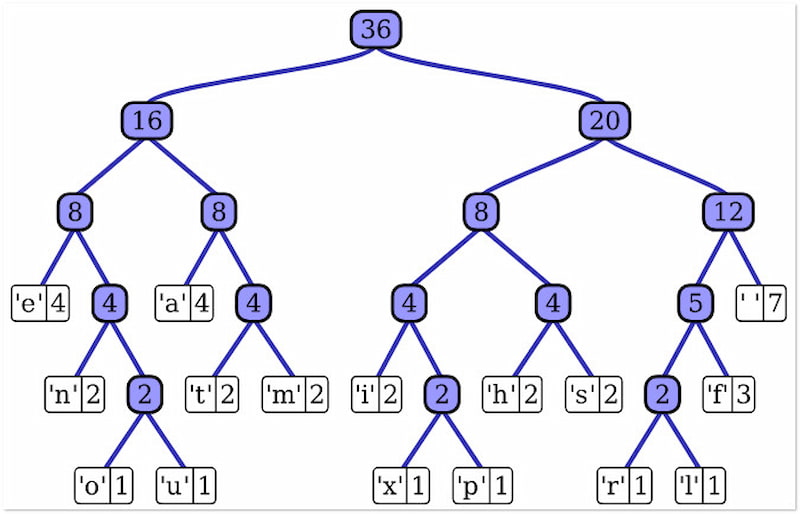
Moving on to our next image compression technique, we have Arithmetic coding. It focuses on assigning shorter codes to more frequently occurring data within an image file. It builds a statistical model of the data and assigns codes based on their probability. This way, frequently occurring data takes up less space in the compressed file.
Deflate
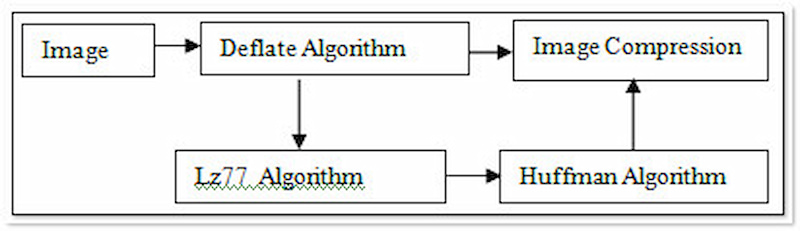
Lastly, let’s talk about Deflate. It combines LZ77 and Huffman coding. LZ77 works similarly to LZW by identifying and replacing repeating data patterns with references. Deflate then utilizes Huffman coding to optimize the code lengths for these references and other data in the compressed file. It is used in conjunction with other methods, such as those in PNG format.
Compression Methods in Different Image Formats
Various image formats adopt different compression methods to optimize file size and quality. These methods can be categorized into lossy and lossless image compression. Each image is designed with specific use cases and uses the most fitted compression technique.
| Image format | Compression Method Used | Details |
| JPEG | Lossy | Uses transform coding, specifically the Discrete Cosine Transform, to transform images into frequency components. |
| PNG | Lossless | Uses the DEFLATE algorithm, a combination of LZ77 and Huffman coding. |
| GIF | Lossless | Uses LZW compression, a dictionary-based algorithm that is effective for images with repeating patterns and limited color palettes. |
| BMP | Lossless Compression | These files are often uncompressed. However, it uses Run-length Encoding for lossless compression. |
| WebP | Lossy and Lossless Compression | For lossy compression, it uses predictive coding. For lossless compression, it employs block splitting and Huffman coding. |
Part 2. How Do I Make the Image Smaller
If you want to make your image smaller in size, Picwand Online Image Compressor is a highly effective tool that you can rely on for such purposes. It is an AI-powered tool that uses a lossless image compression technique to optimize image file size. It can reduce digital image file size by up to 90% while keeping the best quality. For good measure, Picwand Online Image Compressor can handle both lossy and lossless formats. This includes JPG/JPEG, PNG, WebP, GIF, BMP, and more. But what makes it truly remarkable is its simultaneous compression support. It allows you to upload and process up to 20 image files at once.
Why Choose Picwand Online Image Compressor:
◆ Optimize digital image file size without quality loss.
◆ Uses a lossless compression technique powered by AI.
◆ Supports compressing up to 40 image files simultaneously.
◆ Handles both lossy and lossless files like JPEG, PNG, WebP, etc.
Step 1. Reach Picwand Online Image Compressor by navigating to its official website.
Step 2. Click Upload Image(s) to import the images you want to compress. For images from online sources, you can use the drag-and-drop functionality.
Step 3. After importing the images, Picwand Online Image Compressor will analyze them and apply the lossless compression algorithm. So, sit back and wait for the compression to finish.

Step 4. Once the compression process is finished, click the Download All button. A ZIP folder containing the compressed files will be downloaded to your computer.
PicWand Online Image Compressor provides a convenient way for JPG/JPEG, WebP, GIF, BMP, and PNG compression. It ensures that you can get a well-reduced image file without compromising the original quality.
Part 3. FAQs about Image Compression
By what percentage can lossless compression reduce image file size?
Usually, lossless compression can reduce image file size from 10% to 25%. Please note that this compression identifies and eliminates redundant data, not discarding the actual image information. Still, the exact percentage reduction depends on the specific image.
What is the most popular lossless image compression format?
PNG is the most common lossless image compression format. It uses the DEFLATE compression, which is a combination of LZ77 and Huffman coding. This makes it ideal for graphics with sharp lines, text, and logos.
What compression method does a WebP image adopt?
A WebP image adopts both lossy and lossless compression methods. For lossy compression, it uses predictive coding similar to those used in the VP8 codec. For lossless compression, WebP uses block splitting and Huffman coding to compress images without data loss.
Summary
In conclusion, image compression is an essential tool for managing digital image files. It offers several benefits in terms of transmission efficiency and storage. By applying lossy or lossless compression, you can optimize your images for various use cases. If you want to reduce image sizes, Picwand Online Image Compressor can be your companion. It uses a lossless compression technique, ensuring that you’ll get an optimized image file without data loss.
AI Picwand - Anyone Can be A Magician
Get Started for Free